What do De, DN, D, d, and Φ stand for?
Table of contents
- Commonly used pipe specification symbols
- Expression of pipe diameter
- Relationship between nominal outer diameter
- Representation range
Everyday, when designing and purchasing pipes, some users do not express the pipe diameter clearly enough, causing the supply and demand parties to spend a lot of time confirming product specifications during the communication process.
Today we will focus on several standard symbols used daily.
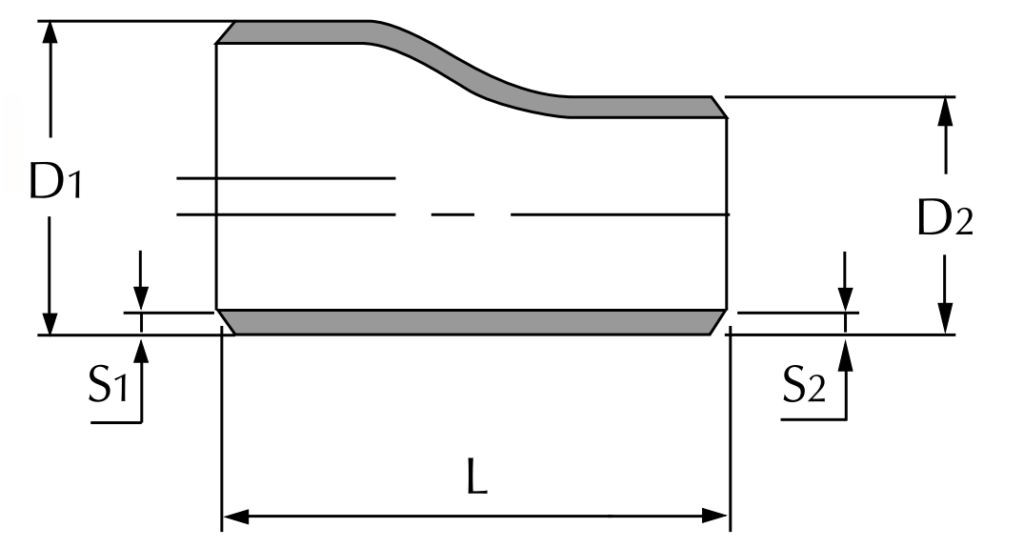
Commonly used pipe specification symbols
Commonly used pipe specification symbols include De, DN, D, d, Ф, etc.
DN
Refers to the nominal diameter of the pipe, which is the average of the outer diameter and the inner diameter. The value of DN = the value of De – 0.5*pipe wall thickness.
NOTE: This is neither the outside nor the inside diameter. Pipes such as water and gas transportation steel pipes (galvanized steel pipes or non-galvanized steel pipes), cast iron pipes, steel-plastic composite pipes and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes should be marked with the nominal diameter “DN” (such as DN15, DN50);
De
Mainly refers to the outer diameter of the pipe, PPR, PE pipe, polypropylene pipe outer diameter, generally used to mark De, all need to be marked in the form of outer diameter x wall thickness, for example De25 x 3;
D
Generally refers to the inner diameter of the pipe;
d
For pipes such as reinforced concrete (or concrete) pipes, clay pipes, acid-resistant ceramic pipes, cylinder tile pipes, etc., the pipe diameter should be expressed by the inner diameter d (such as d230, d380, etc.);
φ
It represents the diameter of an ordinary circle; it can also represent the outer diameter of the pipe, but in this case it should be multiplied by the wall thickness.
For example, φ25 x 3 means a pipe with an outer diameter of 25mm and a wall thickness of 3mm. For seamless steel pipes or non-ferrous metal pipes, “outer diameter x wall thickness” should be marked.
For example, φ108 x 4, φ can be omitted. Some steel pipe standards in China, ISO and Japan use wall thickness dimensions to express steel pipe wall thickness series.
The specifications of this type of steel pipe are expressed as pipe outer diameter x wall thickness. For example φ60.5 x 3.8;
Expression of pipe diameter
Water and gas transmission steel pipes (galvanized or non-galvanized), cast iron pipes, plastic pipes and other pipes should be marked with the nominal diameter “DN” (such as DN15, DN50); De can also be used when wall thickness is involved;
Taking galvanized welded steel pipe as an example, the two marking methods of DN and De are as follows: DN20 De25 x 2.5mmDN25 De32 x 3mmDN32 De40 x 4mmDN40 De50 x 4mm etc…;
For seamless steel pipes, welded steel pipes (straight seam or spiral seam), copper pipes, stainless steel pipes and other pipes, the pipe diameter should be expressed as outer diameter x wall thickness (such as De108 x 4, De159 x 4.5, etc.);
for seamless steel pipes or non-ferrous metal pipes Pipes should be marked with “outer diameter x wall thickness”. For example, φ108 x 4, φ can be omitted;
For pipes such as reinforced concrete (or concrete) pipes, clay pipes, acid-resistant ceramic pipes, cylinder tile pipes, the pipe diameter should be expressed by the inner diameter d (such as d230, d380, etc.);
For plastic pipes, the pipe diameter should be expressed according to the product standard method; usually plastic pipes are expressed according to the outer diameter.
In the actual construction process, the 20, 25, 32 and other pipes we abbreviate refer to De instead of DN. There is one specification difference here. Woolen cloth.
Failure to understand it can easily cause losses during the procurement and construction processes;
When the design uses nominal diameter DN to express the pipe diameter, there should be a comparison table between the nominal diameter DN and the corresponding product specifications.

Relationship between nominal outer diameter
| Commonly known as | inch | DN (mm) | Plastic pipe–nominal outer diameter(mm) |
| 4分 | 1/2 | 15 | 20 |
| 6分 | 3/4 | 20 | 25 |
| 1寸 | 1 | 25 | 32 |
| 1寸2 | 1 1/4 | 32 | 40 |
| 1寸半 | 1 1/2 | 40 | 50 |
| 2寸 | 2 | 50 | 63 |
| 2寸半 | 2 1/2 | 65 | 75 |
| 3寸 | 3 | 80 | 90 |
| 4寸 | 4 | 100 | 110 |
| 5寸 | 5 | 125 | 140 |
| 6寸 | 6 | 150 | 160 |
| 8寸 | 8 | 200 | 225 |
| 10寸 | 10 | 250 | 280 |

Representation range
- De–outer diameter of PPR, PE pipe, polypropylene pipe;
- DN – nominal diameter of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipe, cast iron pipe, steel-plastic composite pipe, galvanized steel pipe;
- φ-Seamless steel pipes or non-ferrous metal pipes should be marked with “outer diameter x wall thickness”, such as: φ108X4.
