A Comprehensive Guide to Concentric and Eccentric Reducers: How to Choose & How to Use
Contents
- Preface
- What is a reducer?
- Types of industrial reducers
- Applications of reducers
- Manufacturing process of reducers
- Concentric reducers vs eccentric reducers
- Selection principles for concentric reducers
- Selection principles for eccentric reducers
- Installation precautions for reducers
- Summary
Preface
Reducers, seemingly simple yet crucial connecting components, play an irreplaceable role. They connect pipes of different diameters, enabling smooth transitions in piping systems, flow regulation, and equipment interface matching.
Understanding the characteristics of reducers can help us operate projects more efficiently. Reading this article will help you gain a more comprehensive understanding of reducers.
If you would like to watch videos about reducer manufacturing, please follow us on YouTube and LinkedIn.

What is a reducer?
A reducer is a pipe fitting used to connect pipes of different diameters or wall thicknesses. It is typically made by connecting two pipes of different specifications.
Reducers ensure a tight and secure connection between pipes, preventing leaks and ruptures, and also improve the flow performance of the piping system.

Types of industrial reducers
Industrial reducers are mainly divided into two types: concentric reducers and eccentric reducers.
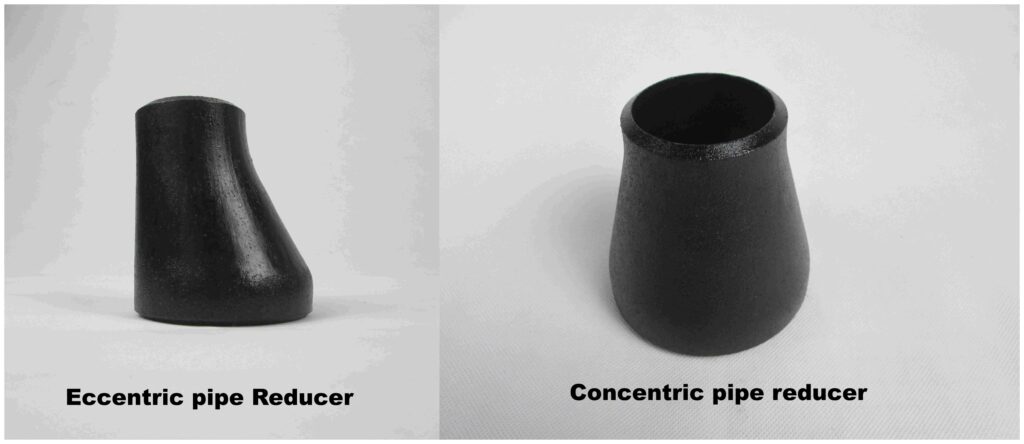
Concentric reducers
Concentric reducers have their centerlines aligned on the same straight line. They are suitable for horizontal or vertical pipelines where the pipe diameter needs to be changed without adjusting the pipe’s center position.
This type reduces fluid resistance and prevents eddies, and is commonly found in liquid transport systems.
Eccentric reducers
An eccentric reducer has its centerlines not aligned, with one side remaining straight. This design prevents gas or vapor buildup in the pipe or avoids sediment buildup in liquid media.
Eccentric reducers are commonly used at pump inlets, in horizontal pipelines, and in systems requiring venting or drainage.
Applications of reducers
Petrochemical Industry: Reducers are widely used in pipeline systems in the petrochemical industry to connect pipes of different diameters, enabling smooth fluid transport.
Water Supply and Drainage Systems: In water supply and drainage systems, reducers are used to adjust pipe diameters to meet varying flow and pressure requirements.
HVAC Systems: In HVAC systems, reducers can be used to adjust pipe diameters to optimize airflow and temperature distribution.

Manufacturing process of reducers
The manufacturing of high-quality reducers requires strict process control and quality management:
Material Selection
Appropriate materials are selected based on the usage environment, and rigorous incoming inspections are conducted to ensure that the material composition and performance meet requirements.
Forming Process
Cold or hot pressing processes are employed, with temperature and pressure parameters controlled during the forming process to guarantee product shape accuracy and surface quality.
Welding Process
For reducers requiring welding, appropriate welding and heat treatment processes are used to eliminate welding stress and improve weld quality.
Surface Treatment
Appropriate surface treatments, such as polishing and passivation, are performed according to usage requirements to improve corrosion resistance.
Quality Inspection
Each batch of products undergoes multiple inspection procedures, including dimensional checks, pressure tests, and non-destructive testing, to ensure that product quality meets standard requirements.

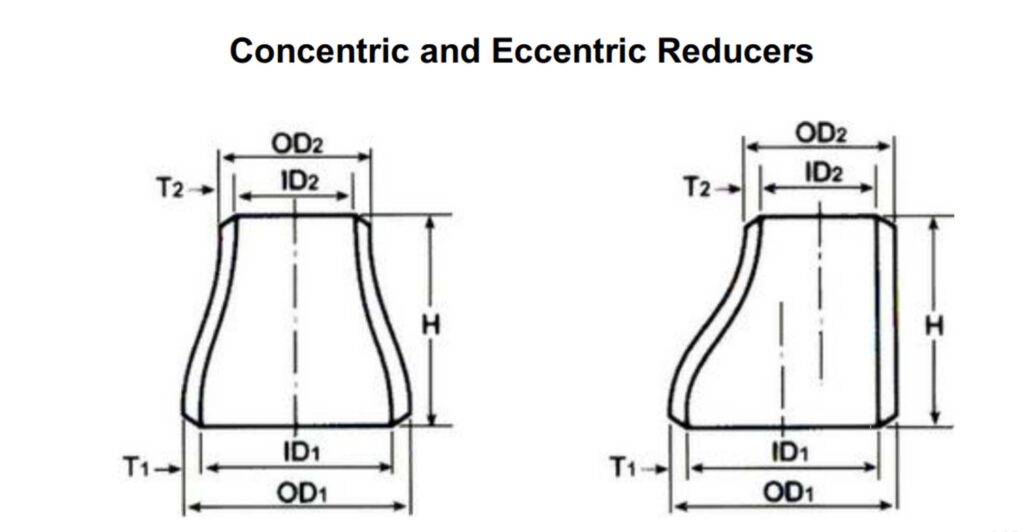
Concentric reducers vs eccentric reducers
Concentric reducers and eccentric reducers differ fundamentally in their structural design and fluid behavior, specifically in the following ways:
Structural differences
Eccentric reducer: The centerlines of the two ends do not coincide, typically with a “flat top and sloping bottom” or “flat bottom and sloping top” design.
For example, an eccentric reducer from DN200 to DN150 has an offset of approximately 10-20mm (refer to ASME B16.9 standard).
Concentric reducer: The centerlines of both ends are perfectly aligned, forming a symmetrical tapered transition, commonly found at the inlet and outlet of pumps and valves.
Influence of fluid properties
The eccentric design can prevent liquid from accumulating at the bottom of horizontal pipes and reduce the risk of cavitation; the concentric design can evenly distribute fluid pressure and reduce turbulence noise.
Selection principles for concentric reducers
Uniform Flow Rate
Concentric reducers are suitable for applications requiring uniform flow rate changes. Due to their symmetrical internal structure, the fluid maintains a relatively stable velocity distribution at the diameter change, which is beneficial for stable system operation.
Low Drag Loss
Compared to eccentric reducers, concentric reducers have a smoother fluid channel, resulting in lower drag loss. This is significant for improving system energy efficiency and reducing operating costs.
Media Cleanliness
For media requiring high cleanliness, concentric reducers are a better choice. Their internal structure makes it less prone to impurity accumulation, thus reducing the risk of contamination.
Standardization and Interchangeability
Concentric reducers typically conform to international standards and industry specifications, offering high interchangeability and versatility.
This facilitates users in selecting and replacing products from different manufacturers, reducing procurement and maintenance costs.
Selection principles for eccentric reducers
Fluid Flow Direction and Pressure Changes
When fluid flows from the larger end to the smaller end, an eccentric reducer can be selected to reduce the impact force or pressure pulsation of the fluid.
This is because the eccentric design allows for a smoother transition of the fluid during the diameter change, reducing the generation of eddies and turbulence.
Space Constraints
In some cases, due to installation space constraints, an eccentric reducer may be necessary to adapt to specific layout requirements. For example, when pipelines need to bypass obstacles or be closely adjacent to other equipment, an eccentric reducer provides a more flexible connection method.
Media Characteristics
For media containing solid particles or prone to sedimentation, an eccentric reducer helps prevent particle accumulation or blockage at the diameter change. By adjusting the eccentric direction, smooth flow of the medium in the pipeline can be ensured.
System Stability
In applications requiring high system stability, such as pump inlets and before and after valves, selecting an eccentric reducer can reduce vibration and noise caused by changes in flow velocity.

Installation precautions for reducers
Before installation, thoroughly remove welding slag and impurities from the inside of the pipes and reducers to prevent blockage or wear.
During installation, ensure proper alignment between the reducer and the pipe, especially for butt-welded connections. Avoid misalignment and forced assembly to reduce localized stress.
For eccentric reducers, pay close attention to the installation direction and strictly follow the design requirements.
Set up appropriate pipe supports near the reducer to support its weight and the forces generated by the flow of the medium.

Summary
As a fundamental yet crucial component in piping systems, the proper application and selection of reducers directly impact the continuity, safety, and energy efficiency of the entire production process.
Through the above article, we have gained a more comprehensive understanding of reducers. If you require further information on reducer pricing, please contact Metleader.
We will provide complete solutions tailored to your project needs to help you meet project requirements more quickly.

