FF Flange VS RF Flange: A Closer Look at Flanges
Table of contents
- Preface
- Flange sealing surface form
- What is RF flange
- What is FF flange
- What does RF10 flange mean
- RF flange vs. FF flange, RTJ flange
- Features of FF flange
- How to distinguish FF flange from RF flange
- FF flange vs. RF flange
- Precautions for FF flange application
- List of China’s top ten flange manufacturers
- Summary
Preface
Flanges are important components in pipeline connections, and their different types of sealing surfaces have different characteristics and applicable occasions.
In low-pressure scenarios, FF flanges gain a firm foothold with their corrosion resistance advantages; when the pressure rises to above 1.6MPa, the stepped sealing design of RF flanges shows strong strength.
The common characteristics of the gaskets of the two flanges provide a flexible solution for engineering selection.
The article focuses on the meaning and difference between the RF and FF surfaces of flanges, which I believe can help beginners.
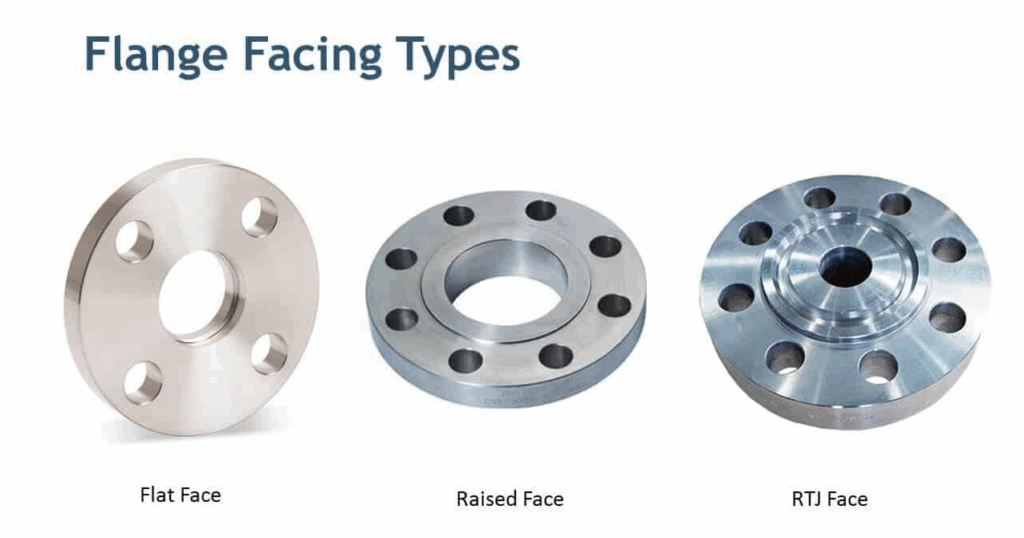
Flange sealing surface form
- Flat surface FF
- Raised surface RF
- Concave and convex surface Raised surface MFM M
- Concave surface FM
- Tongue and groove surface Tenon surface TG T
- Groove surface G
- Ring connection surface RJ
What is RF flange
RF face is a common form of flange sealing surface. The characteristic of RF face flange is that there is a raised annular surface in the middle of the sealing surface, which contacts the gasket to achieve sealing.
Due to its simple structure and easy processing, RF face flange is widely used in medium and low pressure occasions.
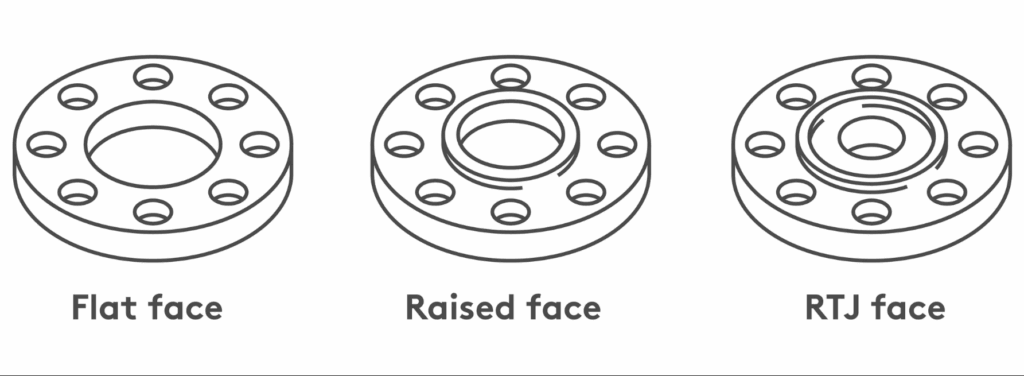
What is FF flange
FF face means that the flange sealing surface is flat, without protrusions or depressions.
FF face flanges are suitable for low pressure occasions or occasions where corrosion-resistant lining rings need to be attached.
What does RF10 flange mean
RF: convex face seal type;
10: American standard flange pressure rating Class 150 (PN20), corresponding to a nominal pressure of about 1.9MPa (refer to ASME B16.5 standard).
This type of flange is commonly used for low-pressure media such as water and steam. The flange outer diameter and the number of bolt holes vary with the size.
For example, the DN50 RF10 flange (2-inch Class 150) has an outer diameter of 165.1mm, 4 bolt holes, and a hole diameter of 19.1mm. Higher pressure ratings such as Class 300 (RF20) require thicker flange necks and more bolts.
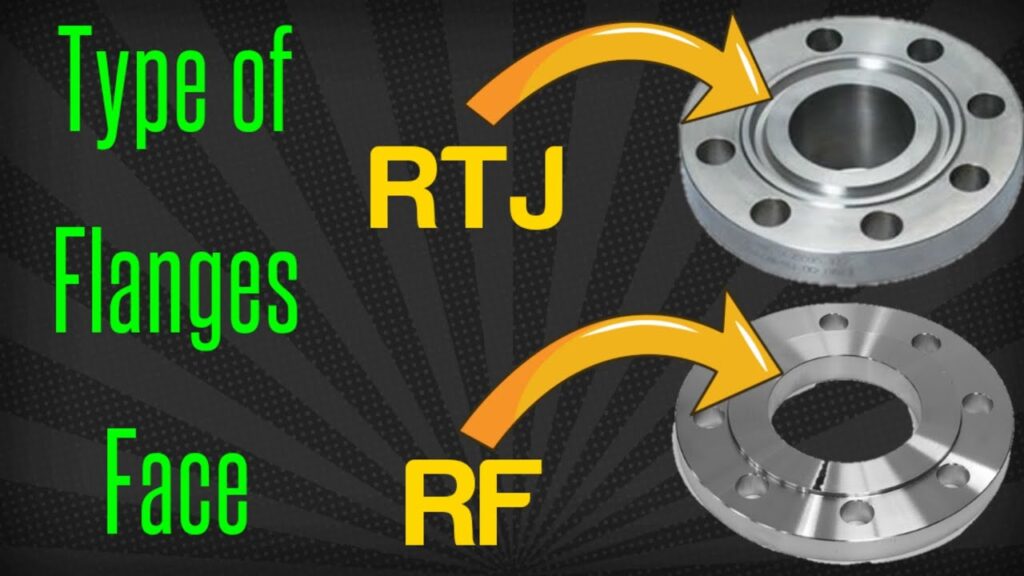
RF flange vs. FF flange, RTJ flange
| Type | Name | Groove Design | Sealing Mechanism | Pressure Rating | Service Conditions | Common Applications |
| FF | Flat Face | Smooth, flat surface | Full-face gasket required | Low pressure | Non-hazardous fluids, ambient temp | Water/air systems, Class 150 flanges |
| RF | Raised Face | Raised circular ring | Gasket within raised area | Medium-high pressure | General industrial services | Process piping (Class 150-600) |
| RTJ | Ring-Type Joint | Groove for metal ring | Oval/octagonal metal ring compression | High pressure | High P/T, critical service | Wellheads, Class 900+ systems |
Features of FF flange
This flange has the following features:
Easy installation: The full-plane sealing surface of the flat welding flange FF eliminates the need for excessive alignment and adjustment during installation, greatly simplifying the installation steps.
Wide range of applications: Due to its low pressure bearing capacity and moderate sealing performance, the flat welding flange FF is widely used in low-pressure, small-diameter pipeline systems, such as construction, water supply and drainage, and HVAC industries.
Economical and practical: Compared with other types of flanges, the flat welding flange FF has a low manufacturing cost and a more affordable price, making it the first choice in many engineering projects.

How to distinguish FF flange from RF flange
There are significant differences between the RF and FF flanges in terms of structure, application and pressure bearing capacity.
To better distinguish them, we can analyze them from the following three aspects:
Differences in sealing surface structure
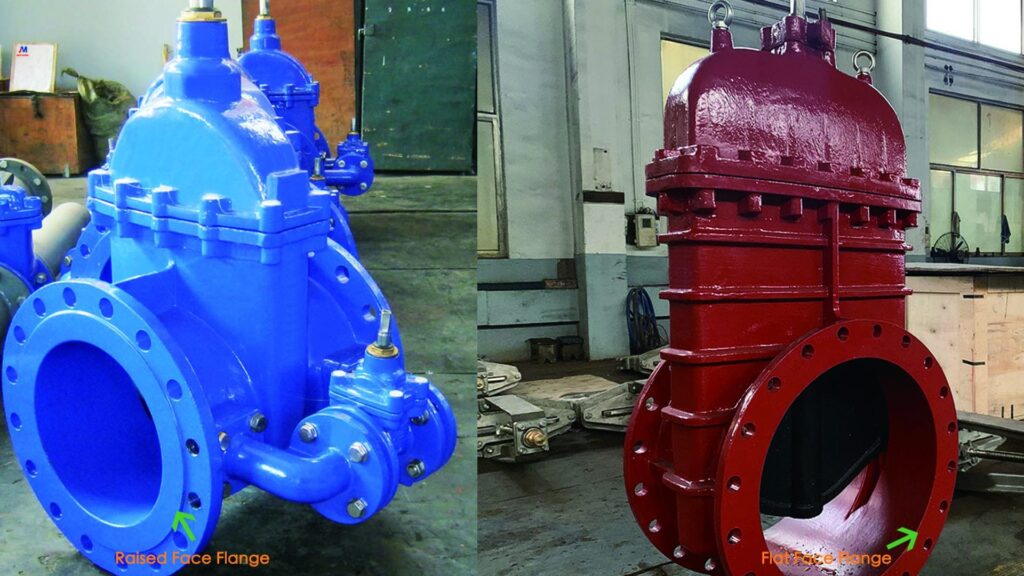
The RF face flange has a raised annular surface, while the FF face flange has a flat surface. This structural difference leads to differences in sealing performance and applicable occasions.
Different sealing principles
FF flanges are evenly distributed on the entire surface, suitable for soft gaskets, and safer in low-pressure scenarios;
RF flanges are concentrated on the bosses, with higher pressure, suitable for metal spiral wound gaskets/graphite gaskets, and better high-pressure sealing;
Different application scenarios
FF surface: used for low-pressure systems ≤ PN16 or fragile pipes (such as fiberglass) to avoid excessive local stress.
RF surface: suitable for high-pressure conditions of PN40 and above, commonly used in petrochemical and nuclear power fields.
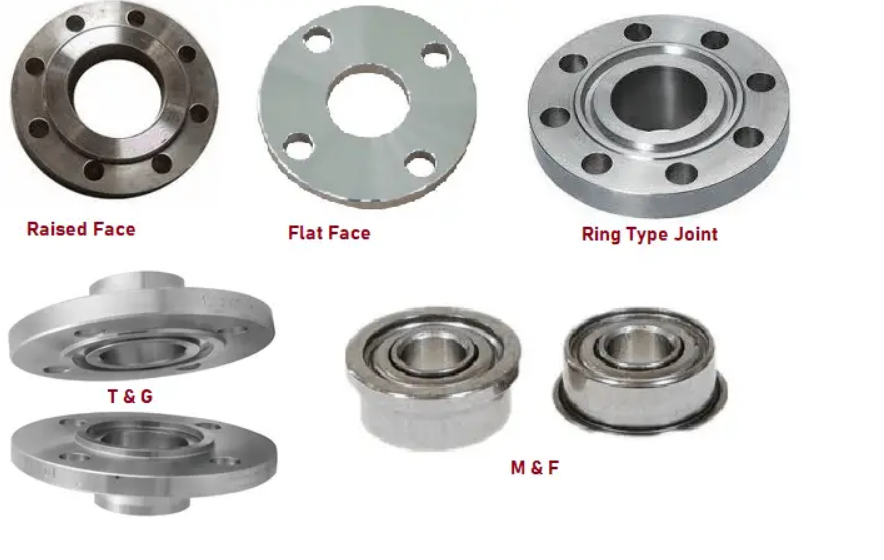

FF flange vs. RF flange
Here’s a detailed comparison between FF (Flat Face) and RF (Raised Face) flanges in English table format:
| Feature | Flat Face (FF) Flange | Raised Face (RF) Flange |
| Face Design | Smooth, entirely flat surface | Central raised circular ring (typically 1.6-6.4mm height) |
| Gasket Contact Area | Full flange face | Only within raised ring area |
| Gasket Type | Full-face gasket (non-metallic: rubber, PTFE, composite) | Ring gasket (spiral wound, metal jacketed) |
| Pressure Rating | Max 150 psi (Class 150) | Up to 2,500 psi (Class 2500) |
| Sealing Mechanism | Uniform compression across entire face | Concentrated compression on raised ring |
| Bolt Load Requirement | Higher (larger gasket area) | Lower (reduced gasket contact area) |
| Vibration Resistance | Poor (gasket creep under cyclic loading) | Excellent (localized compression maintains seal integrity) |
| Temperature Limit | ≤80°C (depends on gasket material) | ≤540°C (with metal gaskets) |
| Material Cost | Lower (simple machining) | Higher (precision machining required) |
| Installation Criticality | Critical flatness tolerance (±0.1mm) | Less sensitive to minor misalignment |
| Common Standards | ASME B16.5, EN 1092-1 Type A | ASME B16.5, API 6A, ISO 7005 |
| Typical Applications | • Cooling water lines • Compressed air systems • Low-pressure vents | • Refinery piping • Steam services • Chemical process lines |
| Prohibited Services | Flammable/toxic fluids (ASME B31.3 prohibition) | None when properly rated |

Precautions for FF flange application
Pressure bearing capacity limitation: The bearing capacity of the flat welding flange FF is relatively low and is not suitable for high-pressure pipeline systems.
Weld quality control: The single-sided welding method of the flat welding flange FF may result in unstable weld quality.
Regular inspection and maintenance: In order to ensure the long-term stable operation of the flat welding flange FF, it needs to be inspected and maintained regularly.
List of China’s top ten flange manufacturers
Here is the list of China’s top 10 flange manufacturers based on comprehensive industry rankings and production capacity:
| Company Name | Founded | Annual Production | Location |
| Wuxi Xilan Flange Forging Co., Ltd. | 1984 | Not specified | Jiangsu |
| Shanxi Guanjiaying Flange Forging Co., Ltd. | 1988 | 30,000 tons | Shanxi |
| Jiangsu Hengrun Heavy Industries Co., Ltd. | 2003 | Not specified (listed: SSE 603985) | Jiangsu |
| Shanxi Tianbao Group Co., Ltd. | – | 60,000 tons (flanges + forgings) | Shanxi |
| Iraeta Energy Equipment | 2006 | 500,000 tons (forgings) | Shandong |
| Shanxi Jinrui High Pressure Ring Co., Ltd. | 1997 | 80,000 tons | Shanxi |
| Wuxi Huaxi Flange Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | 1984 | 25,000 tons (finished flanges) | Jiangyin, Jiangsu |
| MGeldbach (Shanxi) Flange & Fitting Co., Ltd. | 2006 | Not specified | Shanxi |
| Dingxiang Haokun Forged Flanges Co., Ltd. | 1993 | 15,000 – 20,000 tons | Shanxi |
| Shandong Zouping Wangda Forging Co., Ltd. | 2005 | 20,000+ tons | Shandong |
Summary
The article explains RF flange and FF flange in detail, and we have a deeper understanding of these two flanges.
In actual engineering projects, choosing the right flange type and sealing surface form is the key to achieving safe and efficient operation of pipelines.
If you want to learn more about professional knowledge of pipe fittings, please subscribe.