Detailed explanation of blind flange knowledge: a guide to purchasing large projects
Table of contents
- Introduction
- What is a blind flange
- Material of blind flange
- Standards of blind flange
- Characteristics of blind flange
- Application of blind flange
- Pressure level of blind flange
- Difference between blind flange and flange
- Top 10 flange manufacturers in China
- Summary
Introduction
Blind flanges are different from ordinary flanges, and there are also differences in industrial applications.
Flanges are annular connectors, usually with bolt holes, used for detachable connections of pipes, valves or equipment. Blind plates are solid circular plates without center holes, used to close pipe ends or equipment interfaces.
Today, through this article, we will introduce the characteristics, standards and applications of blind flanges to you. Help you better understand all the knowledge of blind flanges.
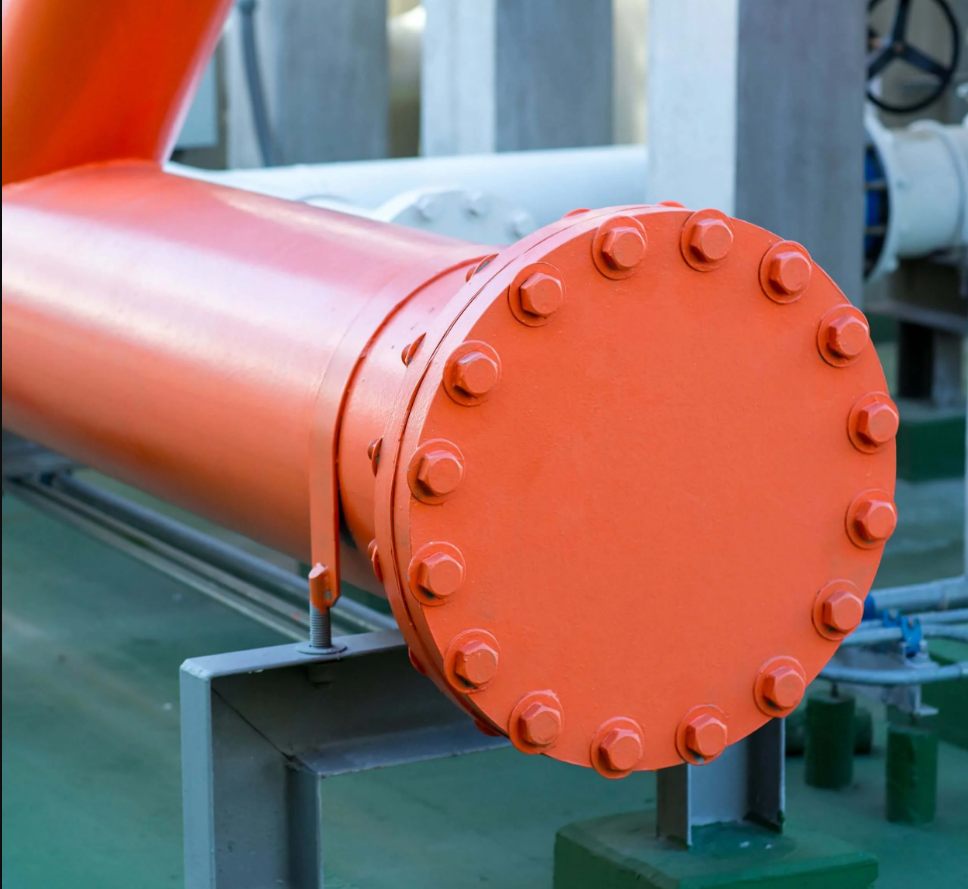

What is a blind flange
A blind flange is a flange used to completely close the end of a pipe in a piping system. It has no central hole and is mainly used to isolate, plug or temporarily close the piping system.
Material of blind flange
The performance of blind flanges directly depends on the material selection. Common materials include:
- Carbon steel (Q235, A105): economical and practical, suitable for general media such as water and air;
- Stainless steel (304, 316L): strong corrosion resistance, used for chemical corrosive media;
- Alloy steel (16Mn, CrMo): resistant to high temperature and high pressure, used in power stations and petrochemical projects;
- Special materials: such as titanium alloy, nickel-based alloy, etc., to cope with extreme working conditions.

Standards of blind flange
- American standard system: ANSI B16.5 (pressure level 150LB~2500LB), API 6A (special for wellhead equipment);
- European standard system: EN 1092-1 (PN6~PN100);
Precision machining requires the roughness of the sealing surface (such as raised surface RF, ring surface RTJ) to reach Ra3.2~6.3μm to ensure a close fit with the gasket.

Characteristics of blind flange
The blind flange has a similar function to the welded cap and threaded cap, and is usually used at the end of the pipeline system or where temporary plugging is required.
The blind flange can be installed by bolts or welding, and is easy to install and disassemble.
During the maintenance and overhaul of the pipeline system, the blind flange can easily cut off the flow of the medium in the pipeline, providing safety protection for maintenance work.

Application of blind flange
Flange connection is widely used as the key connection method for pipeline construction in boiler pressure vessels, petroleum, chemical, shipbuilding, pharmaceutical, metallurgy, machinery and food industries.
Pressure level of blind flange
Blind flanges have a variety of pressure levels and sealing surface types to meet different industrial needs.
In the European system, the pressure range includes PN2.5Bar, PN6Bar, PN10Bar, PN16Bar, PN25Bar, PN40Bar, PN63Bar, PN100Bar, PN160Bar, PN250Bar, PN320Bar and PN400Bar.
In the American system, there are 150LB (approximately equal to PN20Bar), 300LB (approximately equal to PN50Bar), 600LB (approximately equal to PN110Bar), 900LB (approximately equal to PN150Bar), 1500LB (approximately equal to PN260Bar) and 2500LB (approximately equal to PN420Bar) and other pressure levels to choose from.

Difference between blind flange and flange
| Feature | Blind Flange | Standard Pipe Flange |
| Primary Function | Isolate/pressure seal the end of a piping system or vessel opening. | Connect pipes, valves, pumps, or equipment; form a sealed joint. |
| Structure | Solid disc without a center bore. | Ring-shaped with a center bore matching pipe ID. |
| Pressure Boundary | Designed to withstand full system pressure across its face. | Designed to contain pressure within the bore/pipe joint. |
| Installation Context | Installed at termination points or between flanges during maintenance/isolation. | Installed between pipe sections/equipment as permanent connections. |
| Types / Configurations | Flat Face (FF), Raised Face (RF), Ring-Type Joint (RTJ). May be Spectacle (permanent) or Spacer/Lift-off (temporary). | Weld Neck (WN), Slip-On (SO), Socket Weld (SW), Threaded (THD), Lap Joint (LJ), etc. |
| Face Types | FF, RF, RTJ (matches mating flange). | FF, RF, RTJ (determines gasket type/sealing surface). |
| ASME B16.5 Reference | Included (as “Blanks”). | Core scope (defines dimensions, ratings, materials). |
| ASME B16.48 Reference | Core scope (covers pressure ratings, dimensions for Blanks/Spectacle Blinds). | Not applicable. |
| Typical Use Case | • System isolation for maintenance/safety. • Permanent seal on unused nozzles. • Hydrotest/pressure testing. | • Creating continuous pipe runs. • Connecting/disconnecting equipment. • Routing piping systems. |
| Gasket Requirement | Requires gasket between blind and mating flange face. | Requires gasket between two mating standard flanges. |
| Key Distinction | A closure device acting as an end cap or internal seal. | A connecting device facilitating pipeline assembly. |

Top 10 flange manufacturers in China
| Company Name | Founded | Main Products |
| Metleader Pipeline | * | Industrial flanges, pipe fittings |
| Hengrun Co., Ltd. | 2003 | Wind tower flanges, rolled ring forgings |
| Wuxi Huayi Flange Co., Ltd. | 2012 | Carbon/steel/alloy flanges, forgings |
| Hebei Rich Pipe Fitting Mill | – | Slip-on flanges, industrial flanges |
| Epower Metals | – | Long weld neck flanges, threaded flanges |
| Wuxi Huaxi Flange Manufacturing | 1984 | Stainless steel flanges, ring forgings |
| Hebei KaiRui Pipe Fitting Mfg. | 1976 | High-carbon steel flanges, pipe fittings |
| Chengdu ZY-LOC Machinery Tech | 2002 | High-pressure self-tightening flanges (ZY-LOC) |
| Coastal Flange* | – | ASME/DIN standard flanges |
| Guru Gautam Steel* | – | Slip-on/RF/RTJ flanges |

Summary
Blind flange plays a key role in industrial piping systems and is one of the important components to ensure safe and reliable operation of piping systems.
In actual engineering applications, it is necessary to reasonably select the type and material of blind flanges according to factors such as the pressure, temperature, and medium properties of the piping system to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the piping system.
I hope this article can help you understand the knowledge of blind flanges in more detail. If you want to learn more about this, you can subscribe to our youtube and LinkedIn.