Detailed knowledge of alloy steel pipes: everything you can’t miss
Table of contents
- Introduction
- What is alloy steel pipe
- Classification of alloy steel
- Comparison of alloy steel pipe material properties
- Performance of alloy steel pipe
- The influence of different alloy elements on the performance of alloy steel pipe
- Characteristics of alloy steel pipe
- Application of alloy steel pipe
- Grade of alloy steel pipe
- Alloy steel VS stainless steel
- Top 10 alloy steel pipe manufacturers in the world
- Summary
Introduction
Alloy steel pipes are generally made by hot rolling, cold drawing or forging, and are usually used in special environments such as high temperature, high pressure, and corrosion resistance.
In industrial environments, alloy steel pipes are widely used, and alloy steel pipes are used in many large projects.
Among the Fortune 500 companies that Metleader cooperates with, 15.8% of the projects use alloy steel pipes. Below we will introduce alloy steel pipes in detail, hoping to provide you with some help.
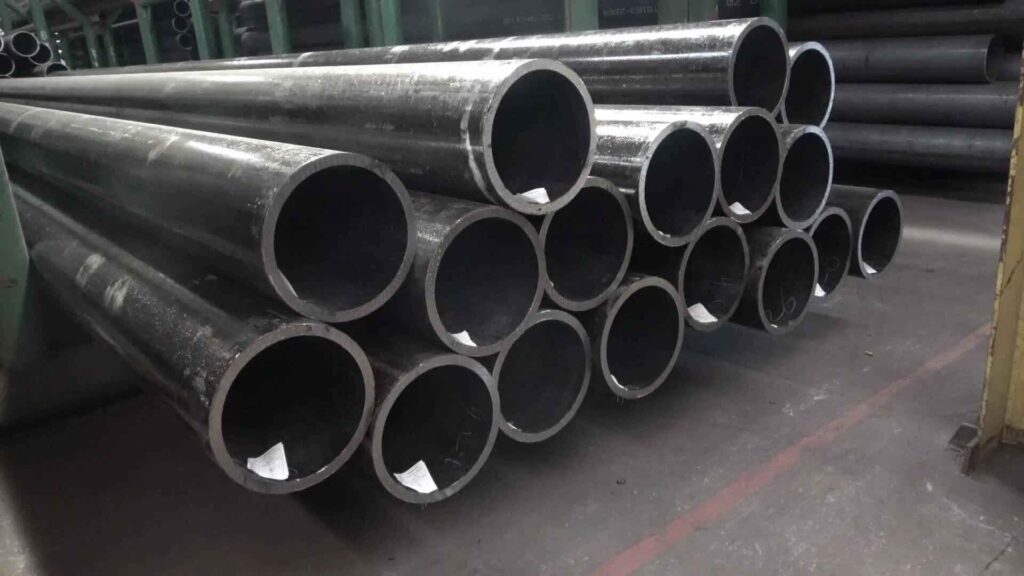

What is alloy steel pipe
Alloy steel pipe is a special steel pipe made by adding one or more alloy elements to carbon steel.
The special properties such as mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and high temperature resistance are improved through alloying.

Classification of alloy steel
Alloy steel pipes are special steel pipes made by adding chromium, molybdenum, nickel and other elements to carbon steel.
Their performance is significantly better than that of ordinary carbon steel. They can be divided into three categories according to the total content of alloy elements:
Low alloy steel
The total amount of alloy elements is less than 5%. Representative materials include 15CrMo (containing Cr 1.0%-1.5%, Mo 0.4%-0.6%), which has high strength and heat resistance and is used in structural parts such as bridges and ships.
Medium alloy steel
The total amount of alloy elements is 5%-10%, such as P91 (containing Cr 8%-9.5%, Mo 0.85%-1.05%), which has excellent creep resistance, high strength and wear resistance, and is suitable for mechanical parts.
High alloy steel
The total amount of alloy elements is greater than 10%, such as 316L stainless steel (containing Cr 16%-18%, Ni 10%-14%), which has outstanding acid and alkali corrosion resistance and is often used in the chemical and aviation fields.

Comparison of alloy steel pipe material properties
The following are the chemical composition and key performance parameters of common alloy steel pipes (taking a steel pipe with a diameter of 50mm and a wall thickness of 5mm as an example):
| Material grade | Main ingredients(%) | tensile strength(MPa) | Applicable temperature | Application |
| 15CrMo | Cr:1.0-1.5, Mo:0.4-0.6 | 440-590 | ≤550℃ | Oil cracking pipeline |
| P91 | Cr:8.0-9.5, Mo:0.85-1.05 | 585 | ≤650℃ | Supercritical boiler |
| 304L | Cr:18-20, Ni:8-12 | 485 | -196~800℃ | Food processing equipment |
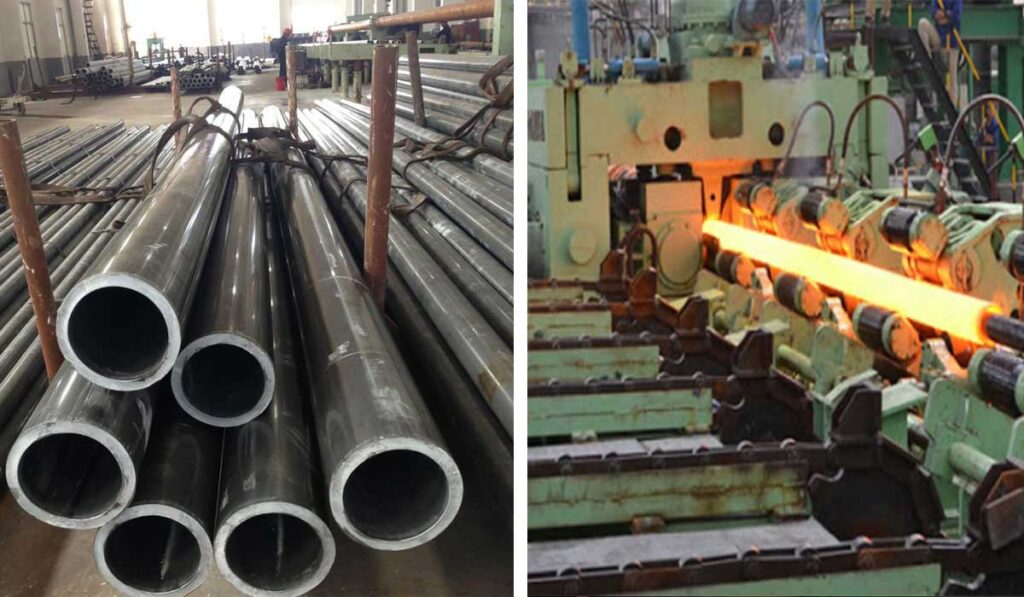

Performance of alloy steel pipe
Alloy steel pipes have the characteristics of high corrosion resistance, high temperature strength and high strength.
They can withstand various harsh environments and withstand conditions such as high pressure, high temperature and strong corrosion.
At the same time, their high melting point, good ductility and high hardness also make them widely used in machinery manufacturing, construction engineering, aerospace and other fields.

The influence of different alloy elements on the performance of alloy steel pipe
- Titanium
Titanium can increase the strength and hardness of alloy steel pipes, improve heat resistance and corrosion resistance, and the amount added should not be too much. - Molybdenum
Molybdenum is mainly used to improve the strength and hardness of alloy steel pipes, and can also increase their corrosion resistance and toughness. - Nickel
Nickel is an important alloying element that can improve the strength and corrosion resistance of alloy steel pipes, and can also resist high temperature and thermal stress corrosion. - Chromium
Chromium is widely used in alloy steel pipes, mainly to improve their oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance, and also to enhance their hardness and strength.

Characteristics of alloy steel pipe
- High strength: Alloy steel pipes have high tensile strength and yield point, and can withstand greater pressure and tensile force.
- High corrosion resistance: Alloy elements can improve the corrosion resistance of steel pipes, especially for corrosive media such as acid, alkaline, salinity and water vapor.
- High temperature adaptability: Alloy elements can improve the high temperature resistance of steel pipes, and can maintain good mechanical properties under high temperature environment.
- Good welding performance: Alloy steel pipes have good welding performance and are easy to weld.
Application of alloy steel pipe
Alloy steel pipes are widely used in the fields of petroleum, chemical industry, aerospace, rail transit, marine engineering, construction engineering, etc.
Among them, in the petroleum and chemical industry, alloy steel pipes are not only used as oil and gas pipelines and steam pipelines, but also can be used in high-demand fields such as oil refining, chemical industry, and natural gas;
In the field of construction engineering, alloy steel pipes are generally used for the structure of buildings and the support and stress-bearing parts of bridges, with safe and reliable performance;
In the field of aerospace, alloy steel pipes can be used to manufacture hydraulic systems, aircraft engines, gas turbine blades and other components.

Grade of alloy steel pipe
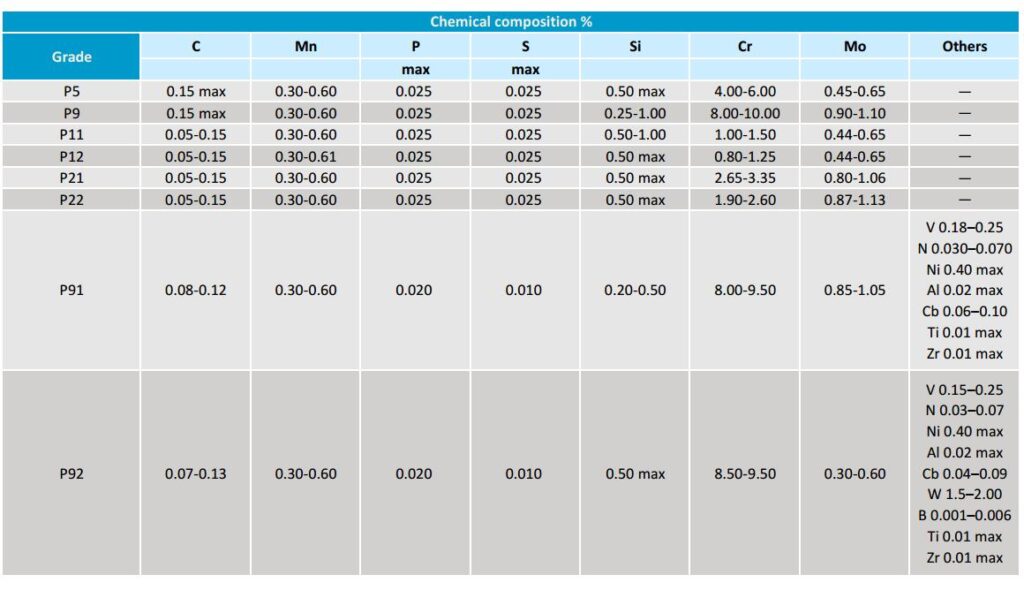
There are several grades of alloy steel pipes, each with its unique properties. The most common grades include ASTM A335, P5, P9, P11, P22, and P91. These grades have different levels of tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and different levels of resistance to corrosion and oxidation.
When selecting the right grade of alloy steel pipe for your application, it is important to consider the temperature and pressure requirements and the type of environment the pipe will be used in.
Alloy steel VS stainless steel
| Parameter | Alloy Steel | Stainless Steel |
| Primary Composition | Iron + Carbon (0.1-1.0%) + Other alloying elements (Cr, Mo, Ni, V) <5% | Iron + Chromium (≥10.5%) + Carbon (<1.2%) + Ni/Mo additives |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (depends on alloy content) | Excellent (passive Cr₂O₃ layer formation) |
| Key Standards | ASTM A335 (P-series), AISI 41xx/43xx series | ASTM A312 (TP-series), AISI 300/400 series |
| Typical Yield Strength | 415-1,380 MPa (varies by heat treatment) | 205-1,100 MPa (annealed condition) |
| Heat Treatment | Requires quenching & tempering for optimal properties | Solution annealing sufficient for most grades |
| Temperature Resistance | Superior high-temp strength (Cr-Mo alloys) | Better oxidation resistance at high temps |
| Magnetic Properties | Generally magnetic | Austenitic (300 series) non-magnetic, others magnetic |
| Weldability | Pre/post-heat treatment often required | Generally good (304/316 excellent) |
| Cost Factor | Lower (except for high-nickel alloys) | Higher (due to Cr/Ni content) |
| Common Applications | Pressure vessels, pipelines, automotive components | Food processing, medical, marine environments |
| Microstructure | Martensitic/Bainitic (after heat treatment) | Austenitic/Ferritic/Martensitic/Duplex |
| Galvanic Corrosion Risk | Higher (unless properly coated) | Lower (self-protecting oxide layer) |
| Machinability | Good (varies with alloy content) | Poor (work-hardens rapidly) |
| Impact Toughness | Excellent at low temps (properly heat treated) | Varies (duplex grades best for cryogenic) |
| Common Grades | 4140, 4340, P91, F22 | 304, 316, 410, 2205 |

Top 10 alloy steel pipe manufacturers in the world
| Rank | Company Name | Location | Main Products |
| 1 | Vallourec | Boulogne-Billancourt, France | – Premium alloy OCTG pipes (API 5CT) – High-temperature nickel alloys (ASTM B407/B423) |
| 2 | Tenaris | Luxembourg | – Seamless alloy pipes for sour service (NACE MR0175) – CRA (Corrosion Resistant Alloy) pipes |
| 3 | Nippon Steel Corporation | Tokyo, Japan | – Cr-Mo alloy pipes (ASTM A335 P11-P92) – Super duplex stainless (UNS S32750) |
| 4 | Sandvik Materials Technology | Sandviken, Sweden | – High-performance alloy tubes (Inconel 625, Hastelloy C276) – Precision cold-drawn seamless pipes |
| 5 | JFE Steel Corporation | Tokyo, Japan | – High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) pipes – API 5L X80-X120 grade line pipes |
| 6 | ArcelorMittal | Luxembourg | – Alloy structural pipes (ASTM A519) – Quenched & tempered pipes for mining |
| 7 | TMK (Трубная Металлургическая Компания) | Moscow, Russia | – Alloy OCTG pipes with internal coatings – Arctic-grade low-temperature alloys |
| 8 | Beijing Metleader Pipeline Technology Inc. | Beijing, China | – Precision alloy steel pipes (ASTM A213/A335) – Corrosion-resistant clad pipes |
| 9 | Salzgitter Mannesmann Stainless Tubes | Salzgitter, Germany | – Austenitic/Ni-based alloy pipes (EN 10216-5) – U-bends for heat exchangers |
| 10 | Jindal SAW Ltd. | Rajasthan, India | – LSAW alloy pipes for power plants – CRA-lined pipes (Inconel 825 clad) |

Summary
As a high-strength, high-corrosion-resistant material, alloy steel pipes are widely used in many fields. Today’s article mainly introduces the basics of alloy steel pipes and high-quality manufacturers around the world.
If you want to learn more about steel pipes, you can follow our youtube and LinkedIn.
