Slip-on flange basics: beginner’s guide
Table of contents
- Introduction
- What is a slip-on flange
- Classification of slip-on flanges
- Specifications of slip-on flanges
- Core features of slip-on flanges
- Applications of slip-on flanges
- Precautions for selecting slip-on flanges
- Slip-on flanges vs. butt-weld flanges
- Slip-on flanges vs. socket-weld flanges
- Top 10 flange manufacturers in the world
- Summary
Introduction
Slip-on flange is one of the most widely used flange types in industrial piping systems. Understanding the basics of slip-on flanges can help us better choose suitable products.
Among the various flange types produced by Metleader, slip-on flange is one of our most important sales products, exported to more than 80 countries, and highly recognized by the market.
In this article today, we will focus on the slip-on flange, hoping to provide some help to beginners.
If you want to know more about flange pipe fittings, please subscribe to our youtube and LinkedIn.

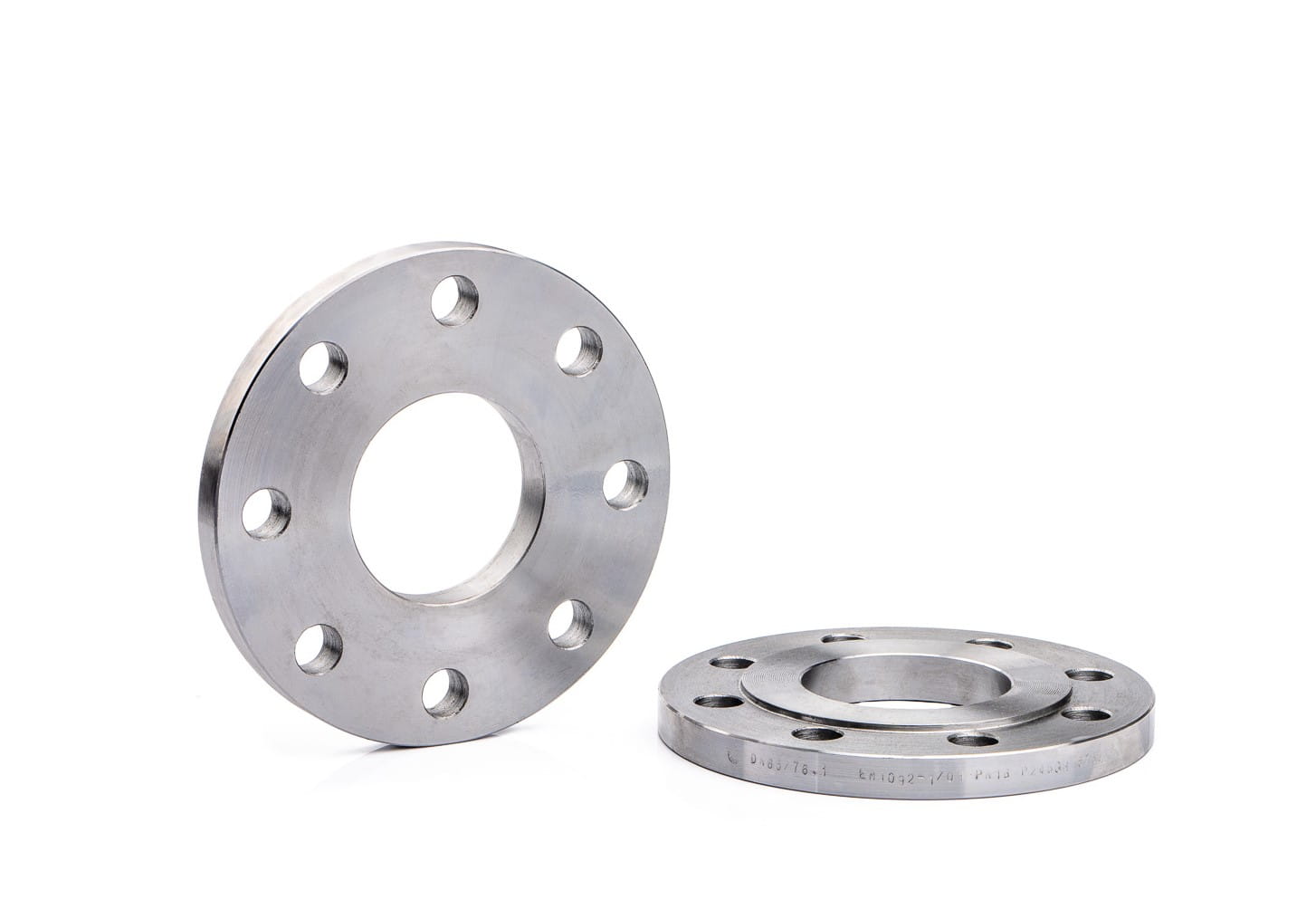
What is a slip-on flange
The flat weld flange is an annular disc-shaped component connected to the pipeline by welding. Its welding surface is flat and only single-sided welding is required when docking with the pipeline.
It is the basic type of flange.

Classification of slip-on flanges
Slip-on flanges used on containers are divided into Type A and Type B.
Depending on the application, they are also divided into steel pipe flanges and necked steel pipe flanges.
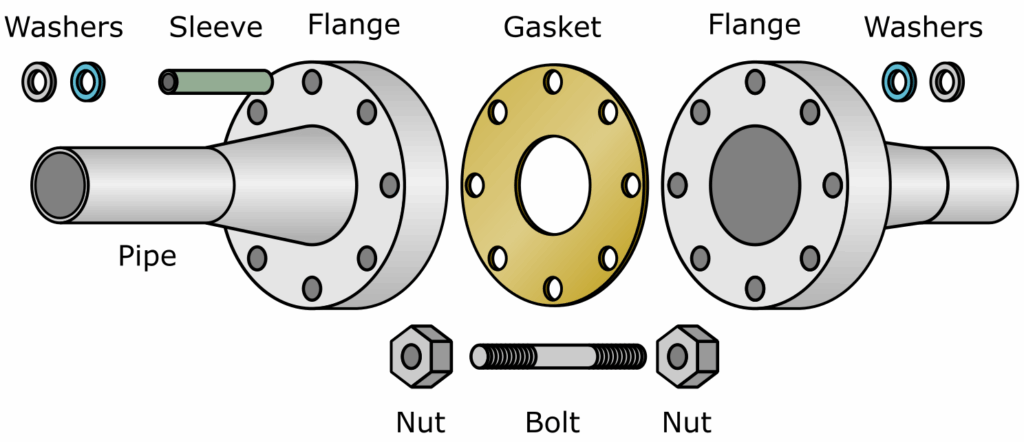
Specifications of slip-on flanges
- Pipe outer diameter: 14-529mm;
- Flange outer diameter: 90-730mm;
- Bolt hole center circle diameter: 60-660mm;
- Flange thickness: 16-52mm;
- Bolt hole diameter: 14-41mm;
- Number of bolts: 4-10;
- Flange theoretical weight: 0.634-67.3kg.
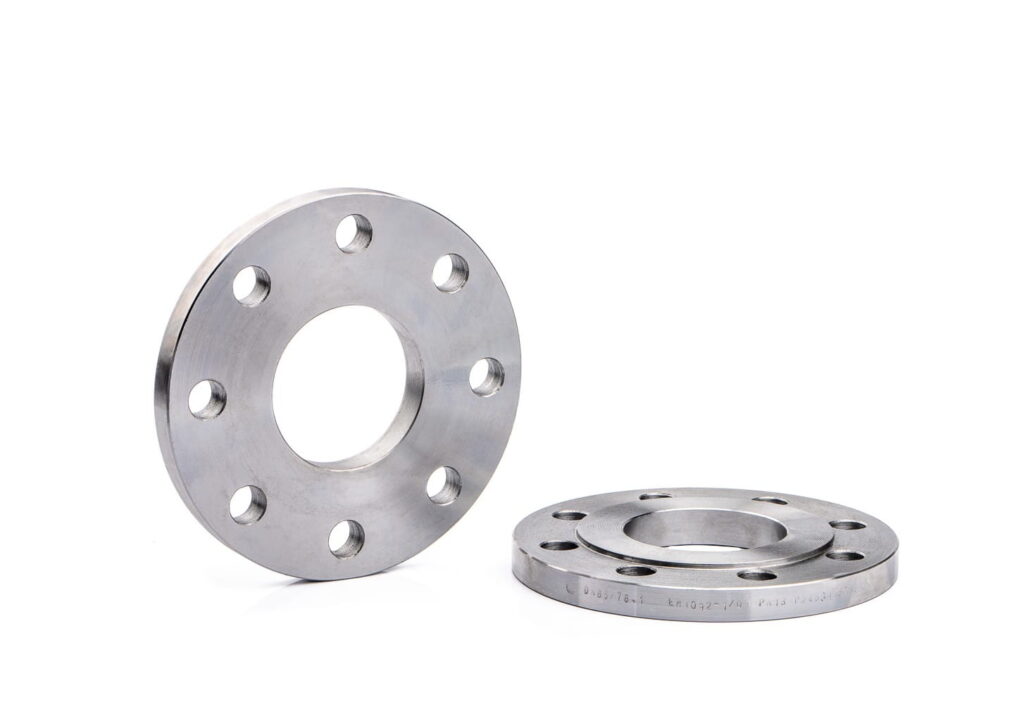

Core features of slip-on flanges
- The design of the flat welding flange saves space, is light in weight, and is easy to install and operate;
- This flange uses a special sealing ring, so the sealing effect is relatively ideal;
- Because the use of the sealing ring reduces the use of bolts, the pressure on the flat welding flange is reduced, so it is not easy to deform and has a relatively long service life.
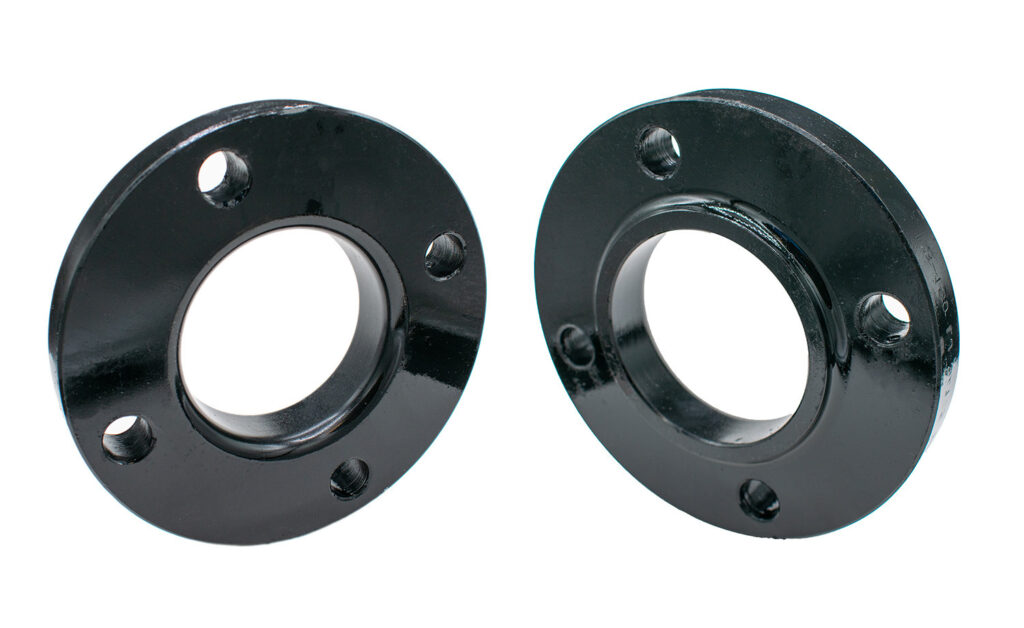

Applications of slip-on flanges
Flat welding flanges have a simple structure, save materials, and are easier to align during welding and assembly, so they are widely used in the connection of medium and low pressure containers and pipelines.
Petroleum and chemical industry: In the process of petroleum refining and chemical production, flat welding flanges are used to connect various equipment and pipelines to ensure the safe transmission of media in pipelines.
Power industry: In power systems, flat welding flanges are often used to connect pipelines of equipment such as boilers and generators, as well as cooling water systems.
Shipbuilding: Various pipeline systems on ships, such as fuel systems and cooling systems, are also often connected with flat welding flanges.
Building water supply and drainage and HVAC: In the construction industry, flat welding flanges are widely used for pipeline connections of water supply and drainage systems and HVAC systems.
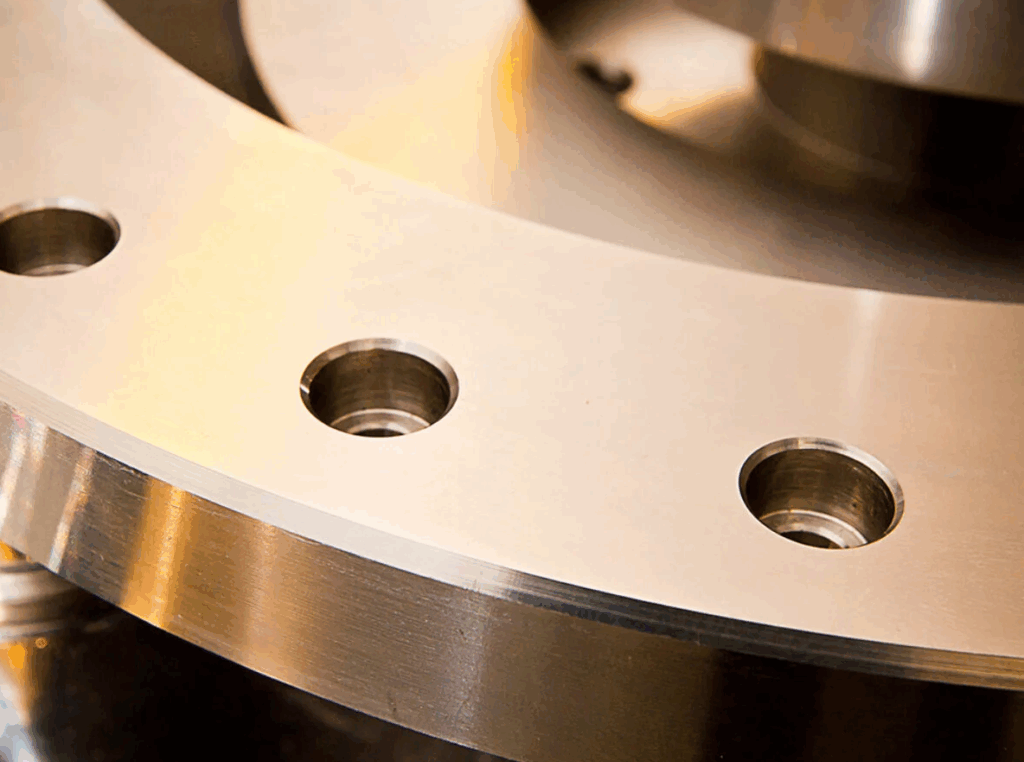

Precautions for selecting slip-on flanges
- Selection basis: Comprehensive judgment based on design pressure, medium corrosiveness and installation space;
- Installation points: Radiographic inspection is required to detect weld quality after welding;
- Alternative solution: If the working condition is close to the critical value, it is recommended to upgrade to a flat-welded flange with a neck, which has a stronger pressure-bearing capacity.
Slip-on flanges vS butt-weld flanges
| Parameter | Flat Welding Flange (FF) | Butt Welding Flange (WN) |
| Structural Design | Flat face without tapered hub; constant thickness | Tapered hub integrated with pipe; reinforced neck transition |
| Welding Method | Fillet weld (external) to pipe | Butt weld (full penetration) at hub + optional external weld |
| ASME B16.5 Classification | Class 150/300 only (limited pressure) | All classes (150 to 2500) |
| Stress Distribution | Concentrated at weld toe (high fatigue risk) | Progressive stress transfer via tapered hub (≤20% peak stress) |
| Pressure Containment | Max 300 psi at 100°F (ASME B31.3) | Full rating per class (e.g., 2500 psi for Class 900) |
| Vibration Resistance | Poor (prone to weld cracking) | Excellent (fatigue life 10× > FF) |
| Installation Alignment | Critical (misalignment induces bending stress) | Self-aligning; hub guides pipe positioning |
| Bore Matching | Requires manual bore adjustment (risk of misalignment) | Seamless bore continuity (reduced turbulence) |
| Material Efficiency | 40–60% lighter than WN (low material cost) | Higher material usage (hub adds 30–50% mass) |
| Temperature Suitability | ≤200°C (thermal cycling causes flange warping) | ≤600°C (tapered hub absorbs thermal expansion) |
| NDT Requirements | Visual inspection (VT) only | Radiography (RT) mandatory for hub-pipe weld |
| Common Applications | • Low-pressure water lines • HVAC systems • Non-critical vents | • Refinery piping • High-pressure steam • Subsea manifolds |
| Cost Comparison | 30–50% cheaper (Class 150) | Higher initial cost (justified by lifecycle performance) |
Slip-on flanges vS socket-weld flanges
| Parameter | Flat Welding Flange (FF) | Socket Welding Flange (SWF) |
| Structural Design | Flat face with no recess; pipe butts against flange face | Counterbore cavity (socket) for pipe insertion |
| Welding Method | Single fillet weld on external face only | Fillet weld on external hub + optional internal weld |
| Pipe Preparation | Square-cut pipe end required | Pipe end must be deburred/chamfered |
| ASME B16.5 Pressure Class | Limited to Class 150/300 | Class 3000/6000 recommended for ≤ DN 80 (NPS 3) |
| Weld Integrity | Low (single weld path; root penetration unverified) | High (dual weld paths; internal support reduces flexure) |
| Gap Requirement | Not applicable | Mandatory 1.6mm gap between pipe shoulder and socket base (ASME B31.3) |
| Bore Alignment | Manual centering required (risk of misalignment) | Self-centering via socket counterbore |
| Fatigue Resistance | Poor (stress concentration at weld toe) | Good (compressive load transfer to flange body) |
| Crevice Corrosion Risk | Low (no stagnant zones) | High (moisture traps in socket cavity) |
| Installation Speed | Faster (single-pass weld) | Slower (gap verification + double welding) |
| NDT Requirements | Visual (VT) only | Liquid penetrant (PT) for hub weld |
| Thermal Cycling Suitability | Poor (differential expansion warps flange) | Moderate (restricted pipe expansion within socket) |
| Maximum Pipe Size | Unlimited (per flange size) | Typically ≤ DN 80 (NPS 3) per ASME B16.5 |
| Typical Applications | • Low-pressure HVAC • Water treatment plants | • Instrument connections • Hydraulic lines • Sampling systems |
Top 10 flange manufacturers in the world
| Company Name | Headquarters | Core Products & Technical Specialization |
| Outokumpu | Espoo, Finland | Super duplex stainless steel flanges (UNS S32750), nuclear-grade corrosion-resistant alloys |
| Sandvik | Sandviken, Sweden | Precision nickel-alloy flanges (Inconel® 625, Hastelloy® C-276) for extreme heat/corrosion environments |
| Metalfar | Barcelona, Spain | API 6A-certified flanges for subsea oil/gas, high-pressure drilling manifolds (15,000 psi rating) |
| Galperti Group | Milan, Italy | Aerospace titanium flanges, modular connection systems with PED 2014/68/EU certification |
| AFGlobal | Houston, USA | High-yield carbon steel flanges (API 5L X80), shale gas fracturing equipment flanges |
| Bebitz Flanschenwerk | Kürten, Germany | EN 1092-1/DIN forgings, nuclear power plant flanges with KTA 3201.4 compliance |
| Beijing Metleader Pipeline | Beijing, China | FBE/3LPE anti-corrosion flanges, precision-machined carbon steel flanges for chemical/offshore projects |
| Viraj Profiles Ltd. | Mumbai, India | Cost-optimized ASTM A182 F304/F316 flanges, mass-produced ASME B16.5 Series A/B flanges |
| Kofco | Seoul, South Korea | Wind turbine tower flanges (EN 10222-3 P460NH), heavy-wall structural flanges (thickness ≤300mm) |
| IPP Group | Istanbul, Turkey | Multi-standard flanges (ASME/DIN/GOST), pipeline fittings for Caspian/Middle East energy projects |

Summary
In this article, we’ve learned some basic knowledge about slip-on flanges, including the differences between them and butt-weld and socket-weld flanges.
If you’re purchasing flanges, we recommend choosing one of the top ten global flange manufacturers for reliable quality.
This concludes our discussion of slip-on flanges today. For more information, visit the Metleader official website.



