Comprehensive Guide to Lap Flanges: Materials, Features, and Specifications
Content
- Introduction
- What is a Lap Flange?
- Classification of Lap Flanges
- Material of Lap Flanges
- Advantages of Lap Flanges
- Applications of Lap Flanges
- Specifications of Lap Flanges
- Lap Flanges vs. Plate Flanges
- Summary
Introduction
Lap flanges are widely used in industrial applications and are essential components in pipelines. But do you know enough about them?
Do you know the difference between a lap flange and a plate flange?
This article details the types, materials, and specifications of lap flanges, hoping to help you choose the right flange for your application.
To learn more about pipe fittings, you can follow us on YouTube and LinkedIn.
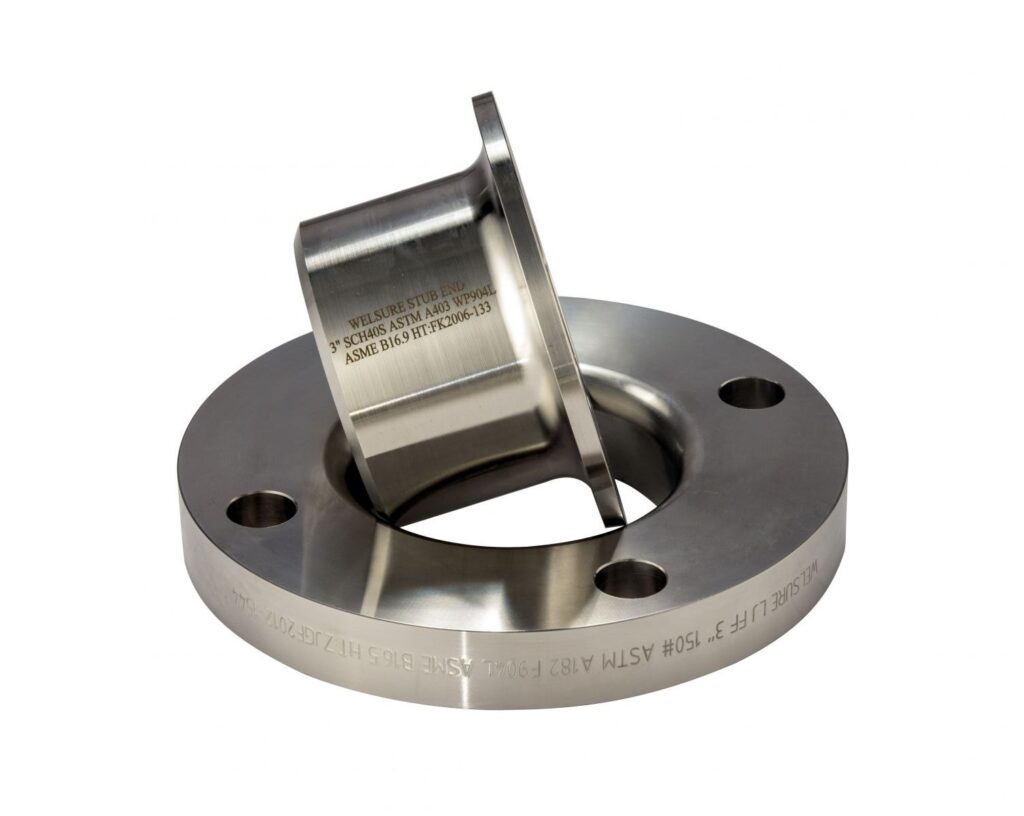

What is a Lap Flange?
A loose flange is a flange used to connect pipes, usually consisting of two flange plates and some bolts.
Classification of Lap Flanges
Loose flanges are widely used in chemical plant pipelines due to their flexible installation and strong vibration resistance.
According to industry standards, they are mainly divided into the following four categories:
Slip-On Ring Lap Flange
Structure: The flange ring is connected to the pipe via a flat weld ring; the flange body is not welded.
Advantages: Low cost, easy installation, suitable for low-pressure, non-corrosive media (such as water and air).
Disadvantages: Low pressure bearing capacity, unsuitable for high-temperature and high-pressure environments.
Butt-Weld Ring Lap Flange
Structure: The flange ring is welded to the pipe using a butt-weld ring, while the flange body remains free to rotate.
Advantages: High strength and excellent pressure resistance, suitable for high-pressure applications such as the petroleum and chemical industries.
Disadvantages: Complex welding process and high cost.
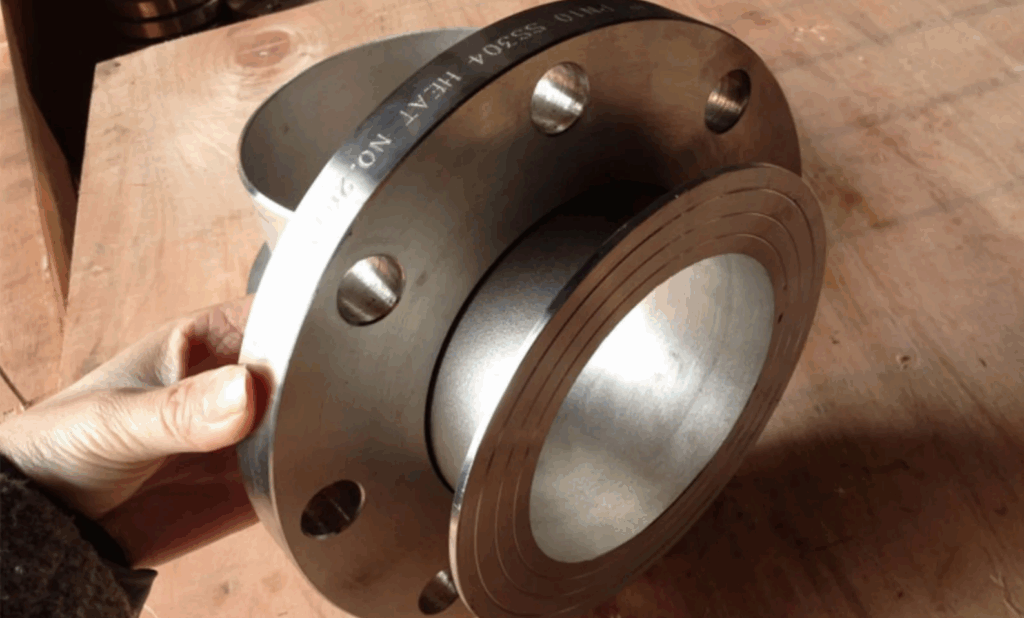

Flanged Flange
Construction: The pipe ends are flanged and fitted with flange rings, which are then secured with bolts.
Advantages: Easy to disassemble and repair, suitable for piping systems subject to frequent maintenance.
Disadvantages: Sealing depends on gaskets, and leakage may occur with long-term use.
Socket-Weld Lap Flange
Construction: The pipe is inserted into the inner hole of the flange ring and welded; the flange ring is not welded.
Advantages: Excellent sealing, suitable for small-diameter, high-pressure pipes.
Disadvantages: Difficult to disassemble after welding, requiring precise alignment.
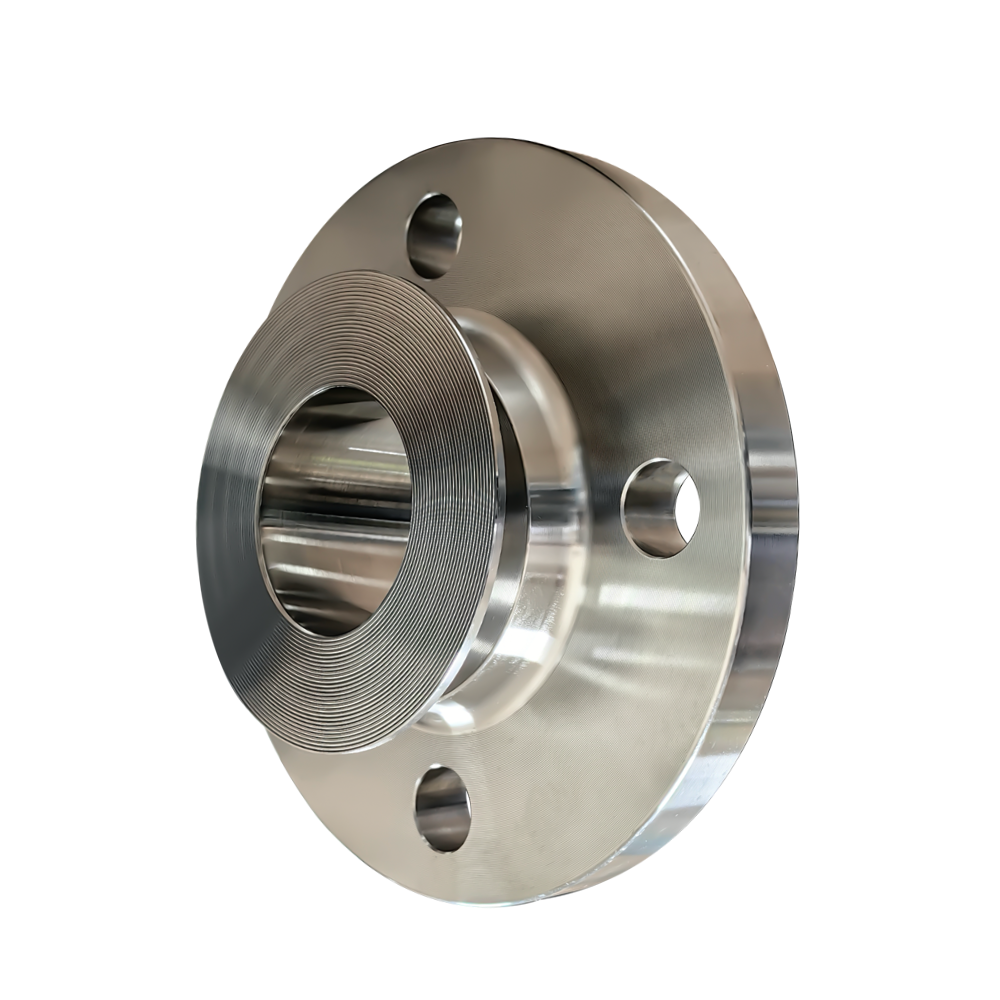

Material of Lap Flanges
The main materials for loose-fitting flanges are:
- Carbon steel
- Stainless steel
- Alloy steel
- Cast iron
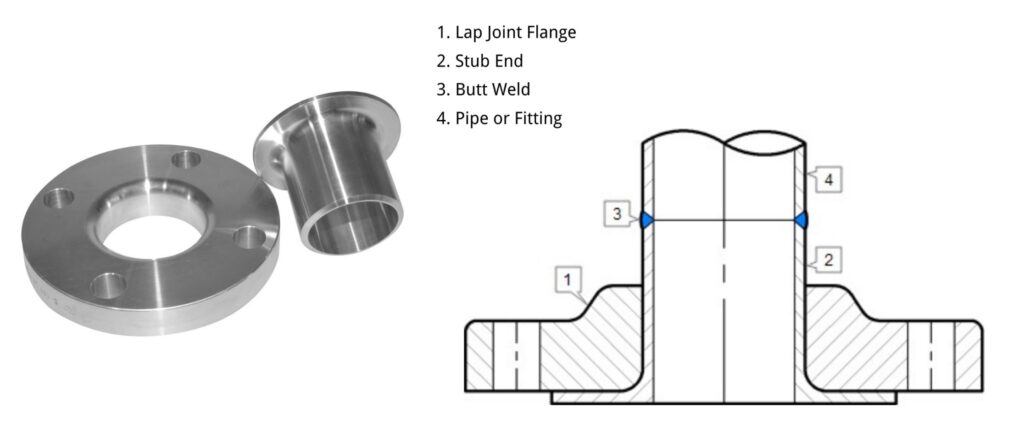
Advantages of Lap Flanges
Excellent Sealing Performance
The sealing surface of a lap joint flange is the same diameter as the pipe, eliminating the risk of gasket loosening or damage. It offers excellent sealing performance and is suitable for complex environments such as high temperatures and high pressures.
Convenient Installation and Maintenance
Compared to butt-weld flanges, lap joint flanges are easier to install and maintain. The use of bolts makes disassembly and replacement easier, reducing labor intensity and maintenance costs.
Wide Applications of Lap Joint Flanges
Lap joint flanges are highly adaptable and can be used with a variety of media and pipeline connection methods. They are widely used in industries such as petroleum, chemical, pharmaceutical, food, and medical.
Applications of Lap Flanges
- Petrochemical industry
- Water treatment industry
- Power industry

Specifications of Lap Flanges
Model | D1 (mm) | D2 (mm) | D3 (mm) | n-φd | L (mm) | H (mm) | Ref. Weight (Kg) |
| DN10 | 90 | 60.5 | 28 | 4-φ14 | 70 | 14 | 0.65 |
| DN15 | 95 | 65 | 34 | 4-φ14 | 75 | 14 | 0.73 |
| DN20 | 105 | 75 | 42 | 4-φ14 | 85 | 14 | 0.85 |
| DN25 | 115 | 85 | 50 | 4-φ14 | 95 | 14 | 0.93 |
| DN32 | 140 | 100 | 66 | 4-φ18 | 115 | 16 | 1.55 |
| DN40 | 150 | 110 | 76 | 4-φ18 | 125 | 16 | 1.72 |
| DN50 | 165 | 125 | 88 | 4-φ18 | 140 | 16 | 1.98 |
| DN65 | 185 | 145 | 110 | 4-φ18 | 160 | 18 | 2.65 |
| DN80 | 200 | 160 | 127 | 4-φ18 | 175 | 18 | 3.02 |
| DN100 | 220 | 180 | 156 | 8-φ18 | 190 | 22 | 4.03 |
| DN125 | 250 | 210 | 184 | 8-φ18 | 220 | 24 | 5.83 |
| DN150 | 285 | 240 | 211 | 8-φ22 | 250 | 26 | 8.26 |
| DN200 | 340 | 295 | 266 | 8-φ22 | 310 | 30 | 12.3 |
| DN250 | 405 | 350 | 324 | 12-φ22 | 370 | 34 | 18.2 |
| DN300 | 460 | 400 | 381 | 12-φ22 | 425 | 34 | 24.6 |

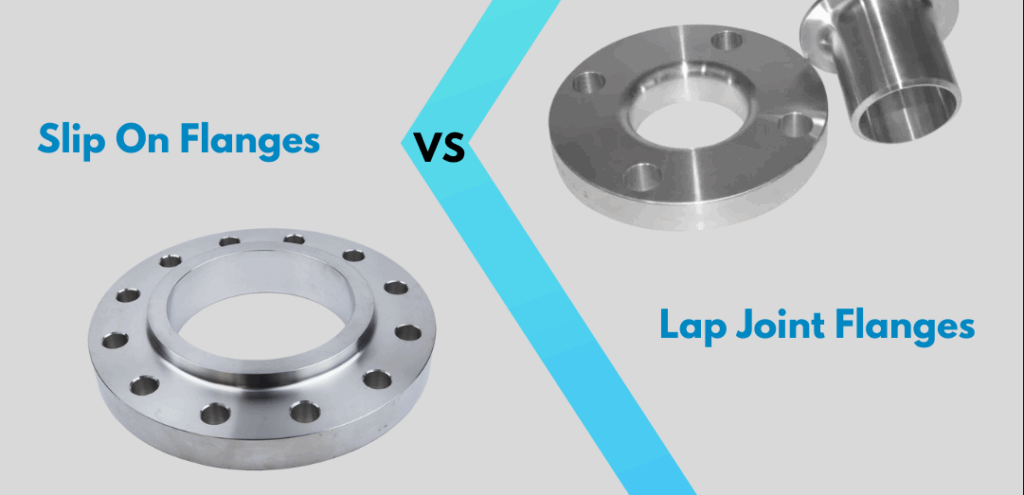
Lap Flanges vs. Plate Flanges
| Feature | Loose Flange | Plate Flange |
| Core Structure | Two components: flange ring + stub end | Single forged/machined plate |
| Sealing Surface | Stub end provides sealing face | Flange face itself seals |
| Pressure Retention | Joint integrity depends on stub end weld | Relies on full-face gasket compression |
| Rotational Capability | Rotates freely pre-tightening | Fixed orientation |
| Parameter | Loose Flange | Plate Flange |
| Piping Alignment | Self-aligning | Requires precise angular alignment |
| Bolt Load Transfer | 100% load on bolts | 70% bolts / 30% flange face |
| Maintenance | Stub end replacement without pipe cut | Full assembly replacement |
| Max Pressure Class | ASME Class 900 | ASME Class 300 |
| Typical Use | Frequent disassembly systems | Permanent low-pressure connections |

Summary
Flanges play a vital role in the seamless operation of pipelines, and their selection depends on a variety of factors, including application, material, cost, and ease of maintenance.
Understanding the differences between lap joint flanges and plate flanges will help you make an informed decision and select the flange type that meets your needs.
Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and hire professionals for installation and maintenance to avoid pipeline accidents and damage.
For the latest flange prices and specifications, please contact Metleader’s sales department.




